voicy
Voice controled telegram bot for Smart Homes
Voicy is a Telegram bot written in python that accepts voice command and execute it using HTTP calls or MQTT topics. Voicy can be easely integrated with HomeAssistant or other Smart Home application that supports MQTT protocol.
Features
- 50+ Supported languages.
- Publish MQTT Topics.
- Send HTTP Post requests (with Headers abd payload).
- Integrate with nodered.
Components and Frameworks used in Voicy
- Loguru
- Google cloud speech
- Wavinfo
- Soundfile
- Wave
- Pydub
- PyYAML
- Numpy
- Requests
- pyTelegramBotAPI
- configparser
- paho-mqtt
Limitations
Speech To Text feature requires active google api cloud account with enabled billing account (pricing table can be found here).
Installation
As I mentioned, in order to use Google Speech Recognition, we need to create Google Application and enable the API. Here are the steps you need to follow to integrate your program with the Google Speech-To-Text API.
Step 1) Create a Google Application, Service account and activate Google speach API
The first thing you need to access Google APIs is a Google account and create a Google application. You can create a google application using the google console: Go to google console.
Once you open the google console, click on the dropdown at the top. This dropdown is displaying your existing google application. After clicking, a pop up will appear, then click on New Project.
Then enter your application name and click on Create.
Once you have created your google application, you need to grant your application access to the Google Cloud Speech-To-Text API. To do so, go to the application dashboard and from there, go to the APIs overview. See below how to access:
Click on Enable Apis and Service, and then search by speech, then all Google APIs to do with text will be listed.
And then click Enable. Once enabled, you will grant permissions to your application to access the Google Cloud Speech to Text API.
The next step is Downloading your Google credentials. The credentials are necessary so Google can authenticate your application, and therefore Google knows that their API is being accessed by you. This way, they can measure how much you are using their APIs and charge you if the consumption passes the free threshold.
Here are the steps to download the google credentials. First, from the home dashboard, got to Go to APIs overview, just like before, and on the left-hand side menu, click on credentials.
Then click on Create Credentials and create a Service Account.
Enter any service account name you like, and click Create. Optional, you can grant service account access to the project, and click Done.
Now click on the service account you just created. The last click will take you to the service account details.
Go to the Keys section and click on Add Key and Create New Key, which will create a new key. This key is associated with your application through the service account.
In the pop-up, select JSON and click on Create, which will download a JSON file containing the key to your machine. Please make a note of where you save this file since you will need it next.
Step 2) Create Telegram bot
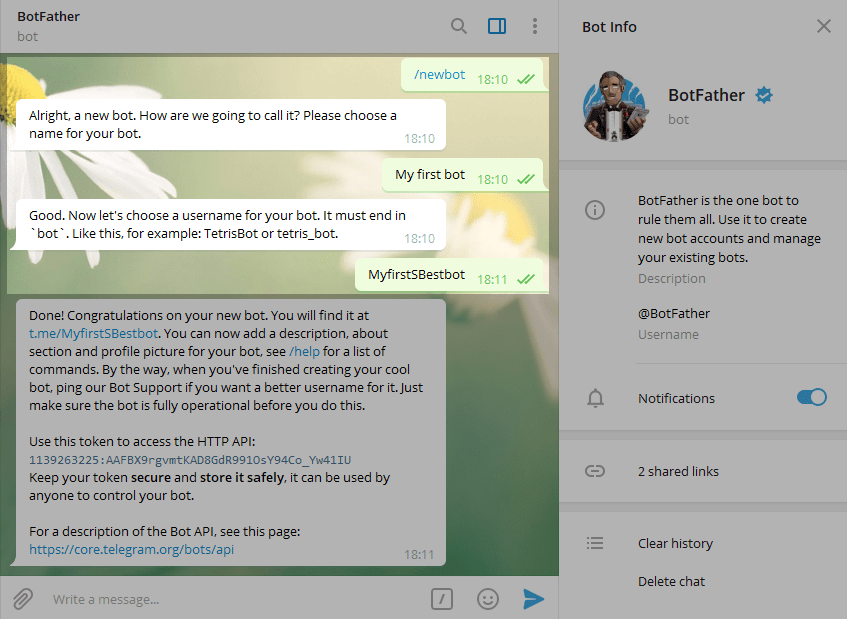
How to Create a New Bot for Telegram Open Telegram messenger, sign in to your account or create a new one.
Enter @Botfather in the search tab and choose this bot (Official Telegram bots have a blue checkmark beside their name.)
Click Start to activate BotFather bot.
In response, you receive a list of commands to manage bots. Choose or type the /newbot command and send it.
Choose a name for your bot your subscribers will see it in the conversation. And choose a username for your bot the bot can be found by its username in searches. The username must be unique and end with the word bot.
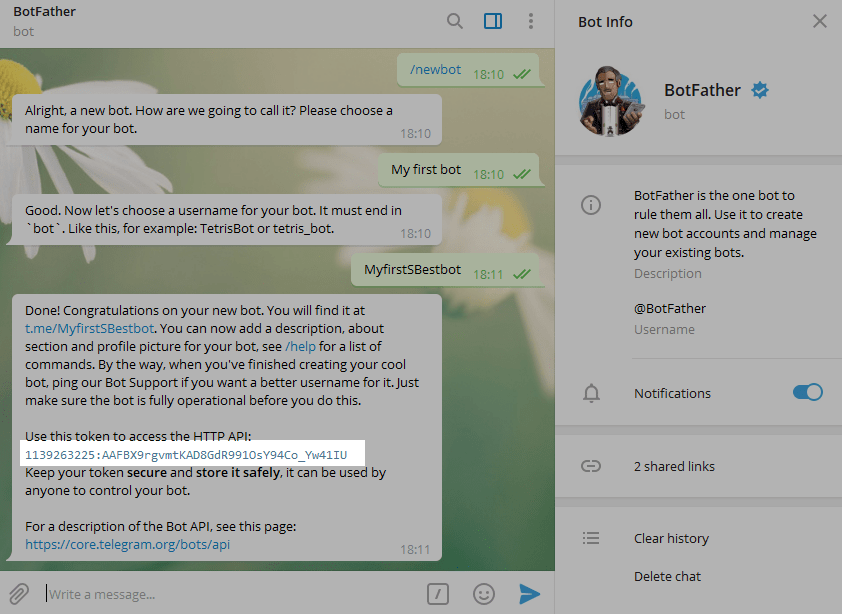
After you choose a suitable name for your bot the bot is created. You will receive a message with a link to your bot t.me/<bot_username>, recommendations to set up a profile picture, description, and a list of commands to manage your new bot.
Step 3) Setup configuration folder
Before we can go and set up the container using docker command or docker-compose we need to set a persistent volume with 3 files in it:
- command.yaml - contains the mapping between voice commands and execution plan sample file. Voice commands not found in the
commands.yamlfile will be forwarded to the default protocol (see config.ini below).
commands:
- name: Boiler on
text: turn boiler on
type: mqtt
topic: voicy/boiler
payload: "on"
- name: Send Post Request with data and headers
text: test post with data and headers
type: post
url: https://webhook.site/0410c31b-5d90-4361-ae0a-1af846efe852
data:
id: 1001
name: geek
passion: coding
headers:
Content-Type: application/json; charset=utf-8
User-Agent: My User Agent 1.0
Authorization: Bearer ABCDEFGH
- config.ini - contains the bot settings (Language, bot token, mqtt broker details) sample file
[Telegram]
bot.token=
bot.allowedid=
bot.welcome.message=Hi, my name is Voicy
[MQTT]
mqtt.host=
mqtt.port=
mqtt.username=
mqtt.password=
[GOOGLE]
speech.language=iw-IL
[Defaults]
default.protocol=mqtt
[RESULTS]
result.ok=
result.error=
- key-file.json - contains the credentials for the google api (Created at step 1)
{
"type": "service_account",
"project_id": "",
"private_key_id": "",
"private_key": "-----BEGIN PRIVATE KEY-----\n \n-----END PRIVATE KEY-----\n",
"client_email": "my-service-account@***.iam.gserviceaccount.com",
"client_id": "",
"auth_uri": "https://accounts.google.com/o/oauth2/auth",
"token_uri": "https://oauth2.googleapis.com/token",
"auth_provider_x509_cert_url": "https://www.googleapis.com/oauth2/v1/certs",
"client_x509_cert_url": "https://www.googleapis.com/robot/v1/metadata/x509/my-service-account-***.iam.gserviceaccount.com"
}
After saving these files, create the following docker-compose file:
version: "3.7"
services:
voicy:
image: techblog/voicy:latest
container_name: voicy
restart: always
volumes:
- ./voicy/config:/app/config
Now, run the following command to install and start the bot:
docker-compose up -d
Once the bot is running, you can intercept voice command transcript mqtt messages in NodeRed using the following flow as base:
[{"id":"ad99fc9b200eb653","type":"mqtt in","z":"9b2c3983f8ebadfa","name":"","topic":"voicy/raw","qos":"2","datatype":"auto-detect","broker":"407a01e4.6b637","nl":false,"rap":true,"rh":0,"inputs":0,"x":120,"y":140,"wires":[["dd67bd29f2e421a7"]]},{"id":"a10f99f03027e442","type":"inject","z":"9b2c3983f8ebadfa","name":"","props":[{"p":"payload"},{"p":"topic","vt":"str"}],"repeat":"","crontab":"","once":true,"onceDelay":0.1,"topic":"","payload":"","payloadType":"date","x":130,"y":60,"wires":[["dfe92e6a8f57dac1"]]},{"id":"dfe92e6a8f57dac1","type":"function","z":"9b2c3983f8ebadfa","name":"set flow utils","func":"flow.set(\"operatorsMap\", (op) => {\n switch(op) {\n case 'on':\n case '':\n return 'turn_on';\n case 'off':\n case '':\n return 'turn_off';\n case 'toggle':\n case '':\n return 'toggle';\n case '':\n return 'close';\n case '':\n return 'open';\n default:\n return op;\n }\n});\n\nflow.set(\"locationsMap\", (where) => {\n switch(where) {\n case '':\n case '':\n return 'salon';\n case '':\n case '':\n return 'basement';\n case '':\n case '':\n return 'all';\n case '':\n case '':\n return 'kitchen';\n default:\n return 'none';\n }\n});\n\nflow.set(\"rawDeviceMap\", (device) => {\n switch (device) {\n case '':\n case '':\n return 'boiler';\n case '':\n case '':\n return 'cover';\n case '':\n case '':\n return 'light';\n default:\n return device;\n }\n});\n\n","outputs":1,"noerr":0,"initialize":"","finalize":"","libs":[],"x":330,"y":60,"wires":[[]]},{"id":"dd67bd29f2e421a7","type":"function","z":"9b2c3983f8ebadfa","name":"analyse","func":"const rawDeviceMap = flow.get(\"rawDeviceMap\");\nconst operatorsMap = flow.get(\"operatorsMap\");\nconst locationsMap = flow.get(\"locationsMap\");\n\nconst [op, what, ...args] = msg.payload.split(' ');\n\nconst commandObj = {\n command: operatorsMap(op),\n device: rawDeviceMap(what),\n}\n\n//handle args\nif (args.length) {\n // check if 1st arg is location\n const where = locationsMap(args[0])\n if (where !== 'none') {\n // a location\n commandObj.where = where;\n } \n}\n\nmsg.payload = commandObj;\nreturn msg;","outputs":1,"noerr":0,"initialize":"","finalize":"","libs":[],"x":320,"y":140,"wires":[["2663f9a6c8a681a3"]]},{"id":"2663f9a6c8a681a3","type":"debug","z":"9b2c3983f8ebadfa","name":"debug 1","active":true,"tosidebar":true,"console":false,"tostatus":false,"complete":"payload","targetType":"msg","statusVal":"","statusType":"auto","x":500,"y":140,"wires":[]},{"id":"407a01e4.6b637","type":"mqtt-broker","broker":"localhost","port":"1883","clientid":"","usetls":false,"compatmode":true,"keepalive":"60","cleansession":true,"birthTopic":"","birthQos":"0","birthPayload":"","willTopic":"","willQos":"0","willPayload":""}]
This flow assumes voice commands of the pattern:
<Operation> <Device> <...Args>
Where args can be location, or any other metadata.
First, on load we inject to the flow context a few functions. This is where you define operations, locations and devices.
Next, we intercept voicy/raw topic messages and analyse the transcript text.
Note: This is a basic flow you should build on, and is not fully operational. Once it determines, for example, "Open covers salon" you should translate that into the proper entity and call the relevant HA service.